The 65nm Socket AM2 AMD Athlon64 X2 4800+ processor
supports X86-64 bit tech, non-executable bit (NX Bit), an integrated DDR2 memory
controller and of course Virtualisation technology.
AMD 32/64 Bit Technology:
 64-bit
processors have registers that hold 64-bit values, double that of 32-bit
processors. This translates to the ability to hold larger integers (numbers) in
a single register, making operations involving massive numbers considerably
faster. It also leads to more precision in floating point numbers, except that
current 32-bit processors already support up to 80-bit floating-point values in
a single register. The major advantage of 64-bit computing is not in
mathematical speed though, but in the amount of memory that a 64-bit processor
is able to address, and consequentially use.
64-bit
processors have registers that hold 64-bit values, double that of 32-bit
processors. This translates to the ability to hold larger integers (numbers) in
a single register, making operations involving massive numbers considerably
faster. It also leads to more precision in floating point numbers, except that
current 32-bit processors already support up to 80-bit floating-point values in
a single register. The major advantage of 64-bit computing is not in
mathematical speed though, but in the amount of memory that a 64-bit processor
is able to address, and consequentially use. Memory addresses are run through the processor just
like any other value, meaning they are stored in the registers. The largest
integer number a 32-bit register can hold is around -2.1 to +2.1 billion. This
translates to a maximum of 4GB of physical memory.
Various work-arounds have been invented
for the server market to transcend this limitation, but all sacrifice
performance. 64-bit registers can effectively address up to 16 terabytes of
physical memory which, to paraphrase Bill Gates, ought
to be enough for anybody.
It should be noted at this point that 64-bit computing is
specific to the operation of the processor and the software that is feeding it,
not the other computer hardware in a system. There are no special '64-bit'
computer memory chips or other peripherals. The AMD Athlon64 X2 4800+ processor
uses the same PC hardware as conventional 32-bit systems. The X2 4800+ is
compatible with both 32/64-bit version of Microsoft Windows XP and Windows
Vista.
 Viruses,
take that!
Viruses,
take that!
The
non-executable bit (or NX Bit) is a form of system security which attempts to
end the possibility of buffer overflow attacks - where malicious software
overloads an area of memory then uses the resulting memory hole to execute alien
programs. It does this by restricting which areas of memory can execute
application code. The NX Bit feature must be supported by both the operating
system and the processor. Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 includes support for it,
as does Windows Vista.
DDR-2 Memory Controller:
All socket
AM2 processors incorporate a DDR-2 memory controller, with an effective dual
channel memory bandwidth of up to 12.8 GB/sec when running dual channel with
DDR2-800 memory.
A single
hypertransport link of up to 8GB/sec between the CPU and motherboard core logic
is supported, so the total CPU bandwidth rounds out to as much as 20.8 GB/s. The
Athlon64 FX and X2 series of AM2 processors will support unbuffered DDR-2 667
& 800 memory (PC2-5300 and PC2-6400 respectively), whereas Athlon64 and
Sempron AM2 chips will operate with more affordable DDR-2 667 RAM.
With the
dual channel DDR2-800 (PC2-6400) installed, the memory subsystem will provide up
to 12.8GB/s worth of bandwidth at any given time, which is exactly what the
bandwidth hungry Athlon64 X2 4800+ processor needs. The Athlon64 X2 architecture
uses a memory controller embedded onto the CPU core, so it also operates at the
CPU clock speed. In other words, there is no delay in moving data from the
processor to the memory controller. Thus the memory controller on the Athlon64
X2 4800+ runs at a full 2.5 GHz
While the
added bandwidth that DDR-2 RAM provides is certainly not going to hinder things,
the 2.5GHz Athlon64 X2 4800+ processor still has a very big sweet tooth for high
quality lower latency DDR-2 RAM. In fact, memory latency has more of an impact
on the socket AM2 processor than memory bandwidth does... as you'll shortly see.
AMD Virtulization Technology
Virtualization technology enables a single computer to run
multiple operating systems and applications in independent partitions. The AMD
socket AM2 Athlon64 X2 4800+ processor support 'AMD Vitualization' technology
in-chip. With virtualization, a computer system can function as multiple
“virtual” systems, the in-chip hardware virtualization logic simply improves
software stability and performance. 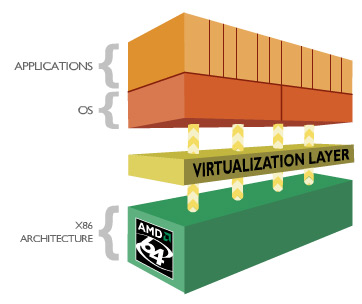
As exciting as this all sounds, the tools necessary to take
advantage of this are absent from the desktop marketplace. Moving the
capabilities of virtualization from software into hardware is seen as a way to
add flexibility into processors, which for the most part aren't seeing demand
increase in step with their clock speeds anymore.
 The main drawback of software
virtualization is that operating systems expect to have exclusive access to X86
architecture. In programming geek talk, OS's require Ring 0 access because
that's what the hypervisor needs, and we all know the hypervisor is the master
OS that hosts all the virtual machines. Uh....right?
The main drawback of software
virtualization is that operating systems expect to have exclusive access to X86
architecture. In programming geek talk, OS's require Ring 0 access because
that's what the hypervisor needs, and we all know the hypervisor is the master
OS that hosts all the virtual machines. Uh....right?
With modern X86 architectures, there are a total of four
ring levels, each of which gives less access to the hardware. For instance,
Windows Vista would run at Ring 0, while Microsoft Word would run at Ring 3.
Less access to the hardware makes sense since it means only the operating system
has control of vital systems. Issues arise with conventional Virtual Machines
when vitalizing another system, because that software program is also an
operating system that is demanding Ring 0 access. As you can imagine, sorting
all this out is why virtualization in software has not really trickled down to
the desktop level.
To circumvent these issues in Windows Vista, the hypervisor
intercept's the Ring 0 code from the virtualized OS and emulates a response.
Unfortunately, this emulation requires a huge amount of computing power, which
when emulating an entire operating system can severely slow a computer system
down.
AMD's hardware Virtualization instructions build in
privileges beneath the Ring 0 level (essentially Ring -1) which is intended to
be used by the virtualization hypervisor. This way the virtualized operating
systems can get Ring 0 access without the need for the hypervisor to interfere.
It also improves performance as there will be less of a need for software
emulation, however it's not completely eliminated since the hypervisor still
needs to juggle the access to the memory controller and I/O between each
virtualized machine.
Next it's time to overclock the AMD Athlon64 X2
4800+!
