What is better, hardware or software RAID? Good question.
It really depends on your means and expectations. Software
RAID setups through an operating system are inherently lower in performance than hardware RAID controllers,
due to the lack of dedicated hardware. They also are, in the case
of Windows XP Pro at least, much easier to set up and much
more flexible in terms of disk use than a hardware based system.
A second factor to consider is whether
you want your operating system disk to be part of the RAID array you create?
A major limitation of the WinXP RAID implementation is that the operating system must be
installed before a RAID array can be created. This means that if you
would like to stripe your operating system disk for increased loading speed, you
are out of luck unless you go with a hardware RAID controller.
So
to cut it short, if you want the maximum benefit out of creating a striped
drive, or need to create a RAID 1 mirror for backups, invest in a motherboard
with an on board RAID controller or a PCI add-on controller card. If you
want to experiment with striped drives for speed, go with the software solution
provided by Windows 2000 or XP as it is easier and cheaper.
How to set up Software RAID in windows XP
Professional
Like most other hard drive and storage options, RAID is managed through Windows
XP's disk management window, found by right clicking on 'my computer,' then
selecting 'manage' followed by 'disk management.' Windows XP Professional
is only capable of creating RAID 0 striped arrays, while the various
Windows Server operating systems can also create software RAID 1 mirror
arrays.
Creating a striped RAID array in XP:
For the purpose of this section of the guide we installed two blank 17GB hard drives on a
test system. To create a striped array you must first have at least two
drives with a portion of 'unpartitioned space' free. The largest stripe
you can create will be twice the size of the smallest unused space on either of
the disks. If you have two disks, one with 4GB of unpartitioned space and
one with 3GB, the largest striped array you could create would be 6GB, as the
area of space used by the stripe on each disk must be the same.
The first step is to convert
both disks from basic to dynamic disks within Windows. A dynamic disk is
a disk that contains an additional database of other dynamic disks
on the system. Dynamic disks can only be read by Windows 2000,
XP Professional and the various Windows Server operating systems, and are required to create
software RAID arrays within Windows.
 For more detail on this subject, see
PCstats' Guide to the little known features of Windows XP.
For more detail on this subject, see
PCstats' Guide to the little known features of Windows XP.
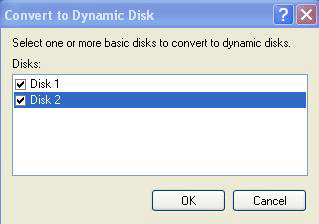
To convert the disks from basic to dynamic, right click the grey box on the
left that contains the disk names (disk 1, disk 2, etc.) and select 'convert to
dynamic disk…'
From the next Window you can check both blank drives and
click 'ok' to convert them.
Once both disks are listed as dynamic, right click the
'unpartitioned space' of either drive and select 'new volume.' On the next page we'll set these drives to be
striped, and configure the software RAID options.

