
|
Broadband technologies such as cable and DSL modems are becoming more popular than ever before, due to their high-speed access and always on connections.
85% Rating: 
|
|
|
|
Home >
Reviews >
Networking >
Netopia R9100 |
|
|
Features Explained
The R9100 contains
several features which may be confusing for those who aren't familiar with the
technology. As such, this section will explain some of the technologies present
in the particular router.
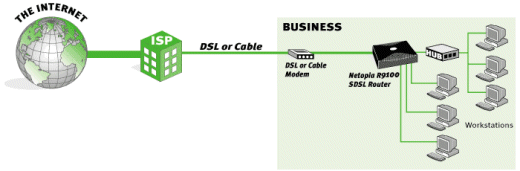
In
order to communicate across a network of more than two people, there has to be a
way to send packets (pieces of information) to the appropriate computer. The
easiest and most cost-effective way to do this is through the use of a hub. A
hub takes the information sent from one computer and broadcasts it to all other connected computers, which can lead to
a rather large amount of network traffic, depending on how many computers are connected at
any given time.
To prevent
this, a switch can be used. Unlike hubs, switches can actually determine where
packets of information need to go on the network, and send them to the right
location without having to do much broadcasting at all. To do this, it uses a
unique code that is burned into every network card called a Media Access Control
(MAC) address. Since each MAC address is different, the switch has no problems
determining where a packet must go, once it determines the MAC addresses of all
connected computers.
Hubs and
switches are fine for inter-network communication, but what about communicating
with other networks? This is where a router comes in. Using a protocol called
RIP (Router Information Protocol), routers are able to determine the best path
to send packets from one network to another. If you've ever tried using the
TRACERT (Trace Route) command in Win9x, you'll see the route that is being taken
to get to a particular location. For example, if you type "tracert
www.PCstats.com" at a command prompt, you'll see all the routers that are used
to connect to our website from your location.
In the
R9100's case, it is mainly designed to pass along packets from your internal
network to the Internet. Back in my article on building a home LAN, I mentioned
a few specific IP address ranges that are considered "non-routable." In essence,
these addresses (such as 192.168.x.x) are ignored by routers, so information
will not be transferred past them.
While on the subject of IP addresses,
another feature of the R9100 is the built-in DHCP server. DHCP, or Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol, is a way of assigning IP addresses to a group of
computers. A DHCP server has a list of IP addresses that are leased to other
clients on the network. The R9100 allows you to set both the IP address ranges,
and the length of time clients may use an IP address before having to renew it
(lease time).
So how can the router be used to actually "share" an
Internet connection? This is done through a process called Network Address
Translation (NAT). When using NAT, the router automatically "translates" any
internal IP address into a single IP address that is visible outside the
network. For example, if you ISP assigns you an IP address of 20.0.0.2, then the
router will automatically convert all address information to that IP. Not only
does this allow the sharing of an Internet connection (as an ISP will only see
the outgoing IP address that it assigns), but it also provides an extra layer of
security. With NAT enabled, any address inside the network is not directly
accessible outside the network. There is a way around this for corporate users
however, and it is called Virtual Private Networking (VPN).
VPN provides
a secure connection for remote users who need access to LAN resources. Unlike
traditional dial-up connections, VPN works over a highly-secure communication
link over the Internet. This makes VPNs a fairly cost-effective solution for
business travellers who are often visiting remote sites, yet still require access
to important documents available on the office network. The R9100 supports
various encryption standards, and can function very well with the included
Dial-Up Networking VPN support found in Win9x and NT. In addition, the router
can replace a dedicated Windows NT server for providing VPN
access.
Finally, to provide a high secure networking environment, the
R9100 has a built-in firewall. Firewalls work on the principle of filter sets,
which define what can leave the LAN, and what can enter. Incoming filters affect
what can enter the LAN from an outside network, while outgoing filters affect
what can leave the LAN onto an outside network. Using filter sets, it is fairly
easy to block access to certain programs such as ICQ or Napster, as you can tell
the firewall to block access to the ports these programs use for
communication.
Now that some of the more advanced terminology relating to
the R9100 has been discussed, it's time to see how easy the router was to
install and configure.
|
