 With the release of the Athlon64 3200+ we are
finally saying good bye to the venerable Socket 462/A platform. AthlonXP 3200's
and Athlon64 3200's may only differ in name slightly, but the physical changes
are enormous. To accommodate the nearly 106 million transistors packed into a
193mm2 die on the Athlon 64 3200+ processor, and the roughly 80W heat output, AMD
have migrated to an entirely new cooling platform.
With the release of the Athlon64 3200+ we are
finally saying good bye to the venerable Socket 462/A platform. AthlonXP 3200's
and Athlon64 3200's may only differ in name slightly, but the physical changes
are enormous. To accommodate the nearly 106 million transistors packed into a
193mm2 die on the Athlon 64 3200+ processor, and the roughly 80W heat output, AMD
have migrated to an entirely new cooling platform.
Larger heatsinks tend to be
more efficient because of larger surface areas, the catch is that along
with a larger heatsink, weight becomes an issue. Keeping that metal mass over the
processor stable used to fall to the socket itself, but we've all heard about
those horror stories.
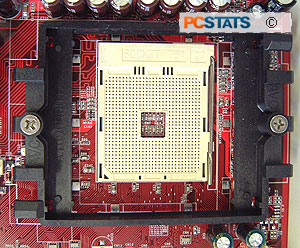
The plastic retention frame now
used with every Athlon64 processor, on both Socket 754 and Socket 940, is made
of glass-filled Lexan, and provides a very firm place for the Athlon64 heatsink to
grip onto. AMD has built the Athlon64 retention frame firmly into its specs, and
there is no getting around that for mainboard manufacturers.
 Given that the reference Socket 754 heatsink
applies upwards of 75lbs force on the Athlon64 processor (to keep the heatsink
in place despite bumps and vibrations, as much as for thermal benefit), there is
one more piece of the equation which is new to the AMD arena.
Given that the reference Socket 754 heatsink
applies upwards of 75lbs force on the Athlon64 processor (to keep the heatsink
in place despite bumps and vibrations, as much as for thermal benefit), there is
one more piece of the equation which is new to the AMD arena.
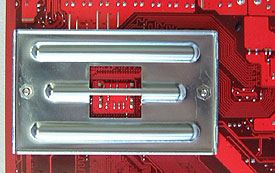
Round back of the motherboard you will find a metal plate about the size
of a deck of cards. It is called the "backplate sub-assembly" and what
it lacks in creative nomenclature, it makes up for in strength.
For if
the metal plate were not placed directly behind the motherboard where the socket
754 socket mounts to the K8T Neo's PCB, the large forces applied by the
heatsink would gradually warp the PCB, and could potentially do enough bending to
break a joint between an IC's solder ball and the trace.
 What does
this all boil down to if you have a nice AthlonXP heatsink collection?
To be blunt, you're out of luck. The old Socket A heatsinks are of
absolutely no use on the K8T Neo-FIS2R or any other Athlon 64 motherboard.
What does
this all boil down to if you have a nice AthlonXP heatsink collection?
To be blunt, you're out of luck. The old Socket A heatsinks are of
absolutely no use on the K8T Neo-FIS2R or any other Athlon 64 motherboard.
The new
heatspreader which covers the fragile silicon
of the processor measures 37mm x 37mm in diameter (larger even then the P4),
and the socket 754 retention frame is incompatible with the older spring clips.
There is one exception at the moment, and that comes from Zalman in the form
of their CNPS700A-Cu heatsink which is compatible with socket A, socket m478, and socket
754 processors.
