By now I'm sure you've heard of SOI and about the problems
AMD has had adopting this new technology. AMD believes so much in SOI that
they've even paid IBM $20 million to help them out. SOI technology allows for
silicon to run at higher frequencies while using less voltage than conventional
silicon like that found in Intel processors or AMD's own K7 line of
CPU's.
 To understand SOI, you must first
understand what a transistor is and how it functions. A transistor is a simple
switch and it can either be on or off (on allows electricity to flow, off
doesn't). When we quote the number of transistors in any given processor (the
Athlon64 has 105.9 million), we're basically describing the number of switches
the processor has.
To understand SOI, you must first
understand what a transistor is and how it functions. A transistor is a simple
switch and it can either be on or off (on allows electricity to flow, off
doesn't). When we quote the number of transistors in any given processor (the
Athlon64 has 105.9 million), we're basically describing the number of switches
the processor has.
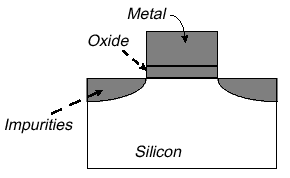
All modern transistors (even SOI enhanced ones) are based
MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technology. MOS means that a piece of metal is
placed on an oxide which is itself a piece of silicon. Pure silicon does
not conduct electricity so impurities are
added which then allow the silicon to be conductive.
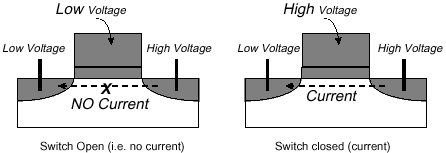
When high voltage is passed through the metal gate, the
silicon becomes conductive and will allow current to pass through it, when the
voltage is low, the silicon becomes an insulator. This is where the term
"Semiconductor" comes from.
SOI and AMD
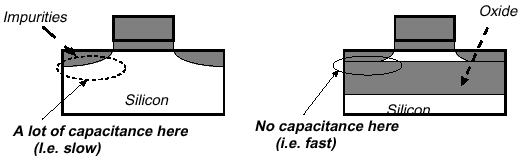
SOI is significant because in theory it will allow
transistors to act much faster when switching between on and off, and
has actually been under development for the last 30 years. SOI literally means
that manufacturers will place a piece of silicon on top of an insulator (glass,
silicon oxide, etc) then the transistor would be placed on top of the SOI. SOI
reduces capacitance, and that makes switches operate faster, and
that allows the electricity get from point-to-point with less of
lag.
So simple. Yet so hard to implement. We're not going
to dwell on how SOI is implemented on a processor as that is beyond the scope of
this review.
