
|
Like AMD's Hypertransport
technology, PCI Express is a 2-way, serial connection that carries data in
packets, similar to the way it is transferred over Ethernet
connections.
|
|
|
|
Home >
Reviews >
Video Cards >
PCI Express Org |
|
|
Videocard Capabilities
Currently, PCI Express X16 provides up to 75W of power
for video cards, as opposed to the current 25W/42W allowed by AGP8X. Most modern
cards already consume
more than this amount, as evidenced by the extra power connectors that appear on
today's AGP high-end video cards. This explains why most modern midrange PCI-Express videocards do not
require extra power connectors, while their AGP counterparts do.
Given that both ATI and Nvidia have virtually switched over to PCI Express and that major graphics companies from 3Dlabs to XGI have already announced support for the architecture, it looks like AGP's days are inevitably drawing to a close. To further depreciate the value of your very
expensive AGP cards, PCI Express X16 and 8x AGP slots cannot coexist
properly on the same motherboard. This fact has not stopped various motherboard
manufacturers from releasing ersatz PCIe/AGP solutions that use the PCI
bus or part of the PCI
Express bus. While this provides a better incentive to upgrade for AGP
card users, it should be noted that these solutions do not provide the full
bandwidth of a real AGP8x slot.

What makes up the PCI Express
bus?
The PCI Express bus is composed of multiple lanes of point-to-point wired copper interconnects serving all
the components that used to just drop data into the older
PCI bus. To make things even more flexible, a switch has been
added to the architecture.
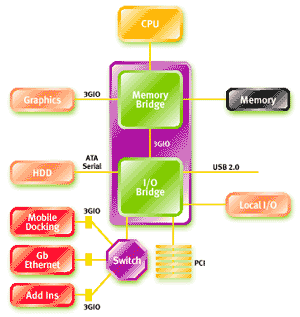
Working in principle just like an Ethernet switch, this sits between the
PCI Express devices connected to the board and the rest of the I/O system. This
will enable newer devices, for example PCI Express connected on board Gigabit controllers or 10/100 gigabit network
cards, to communicate with each other directly if necessary. By adding
in this shortcut the data need not go through the chipset to
reach an adjacent device.
|
