Compared
to the Internet connection sharing method implemented in Windows 98 and ME, the
ICS in 2000/XP is extremely simple and easy to use. Simply designate a
connection to share, set the other computers to obtain an IP address
automatically, and the OS will do the rest. Microsoft apparently realized that
the method they used in their previous operating systems was not exactly idiot
proof.
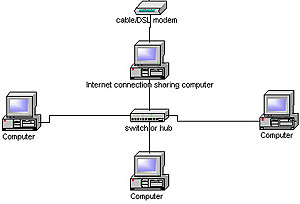
Windows XP/2000 internet
connection sharing works by setting the gateway computer up as a DHCP server and
assigning IP addresses and default gateways to all computers in the network.
Like a router, it will receive messages from inside the network destined for the
Internet, pass them through and listen for the response, then route that back to
the correct computer. Here's how to do it.
First off, the catch. You will
need a second network adaptor in the computer that will act as your gateway,
unless you have an internal or USB cable/DSL modem.
You need to make sure now that all of the computers on your
home network are set up to receive information from the gateway computer. To do
this, the network adaptor in each computer connected to the gateway must be
set to the 'obtain an IP address automatically' setting.
You must have performed the steps listed in the 'setting up client computers'
section of this article above, in order to proceed.
Assuming that the client
computers are set up, it's time to configure the gateway computer. For a WinXP
system, go to start/control panel/network and Internet connections/network
connections and select the icon for your Internet connection.
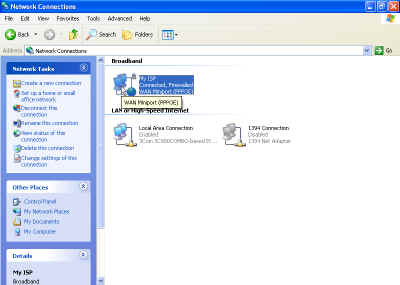
Right click and hit
'properties', then advanced.
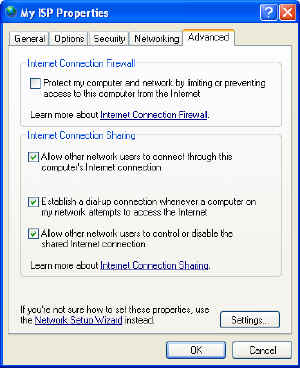
Check the 'allow other
computers to connect through this Internet connection' box. This will enable the
gateway computer to begin handing out IP addresses to your network. Check the
'establish a dial-up connection whenever a computer on my network wishes to
access the Internet' box if you are using DSL and wish to use dial-on-demand.
After 5 minutes or so, all client computers on your network
should have picked up an IP address in the 192.168.0.xxx
range from the gateway, which assigns itself the address 192.168.0.1.
You can speed the process along by typing 'ipconfig /renew' from
the command prompt (start/run 'cmd') on XP or 2000 boxes, and 'ipconfig
/renew_all' on 98/ME systems (start/programs/ms-dos prompt). All systems on your
network should now have Internet access through your gateway computer.

